When your child’s challenging behaviors interfere with learning, their daily routines, or their basic safety, this can quickly feel overwhelming for families, especially families raising a child with autism who may struggle with communication, transitions, or sensory regulation. A behavior intervention plan, ABA approach, provides a structured, evidence-based plan to understand why behaviors happen, and how to support positive change. In ABA therapy, a behavioral intervention plan (BIP) is often mistaken for a punishment plan; instead, it’s a roadmap designed to teach safer and more effective skills based on the function of the behavior.
Designed by trained professionals, usually after a thorough assessment, a BIP ABA framework is intended to help children succeed across several environments, such as home, school, and the community. When implemented regularly, these plans can reduce frustration, increase communication, and improve the quality of life for the rest of the family. Many families first learn about BIPs through ABA therapy or while working with a BCBA therapist, and understanding how they function is the most important step.
What is an effective behavior intervention plan BIP in ABA?
A behavior intervention plan ABA, is a personalized, data-driven strategy used in ABA therapy to reduce challenging behaviors, while teaching appropriate replacement skills. In autism treatment, BIPs are commonly used to address behaviors related to communication breakdowns, sensory sensitivities, rigid routines, or difficulty with transitions.
An effective BIP is created through a structured process that includes a functional behavioral assessment (FBA), clearly defined goals, and evidence-based intervention strategies tailored to your child’s unique needs. A certified ABA therapist uses a behavior intervention plan to establish consistency, guide caregivers and educators, and ensure everyone involved responds to the behavior in a predictable and supportive manner. Over time, this approach can lead to greater independence for the child involved.
Essential Elements of an Effective Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) in ABA Therapy
The foundation of a successful ABA behavior plan lies in its core components. It’s these elements that ensure the plan is clear, measurable, and responsive, which is especially important for autistic children who benefit from predictability and consistency.
Essential elements include the following:
Operational Definitions ABA
The success of any plan depends on precise definitions. Operational definitions in ABA guarantee that behaviors are defined in observable, measurable terms, including frequency, duration, and intensity, rather than broader ones, such as “noncompliant” or “aggressive.” It’s this clarity that allows caregivers, ABA professionals, and teachers to respond appropriately to the child and track meaningful change over time.
Function-Based Intervention Strategies
A strong and effective BIP begins with a good understanding of the relationship between FBA and BIP development. One of the strengths of a fundamental behavioral assessment is that it identifies the patterns between triggers, behaviors, and consequences. In turn, this allows ABA professionals to create strategies that directly address the behavior’s function. These strategies may include reinforcement, environmental adjustments, or teaching the child new skills that better meet the same need. Many plans rely on principles such as ABA positive reinforcement to be delivered before challenging behavior occurs.
Replacement Behaviors and Skill Building
As opposed to simply reducing problem behaviors, a behavior intervention plan, ABA, emphasizes teaching replacement behaviors. For children with autism, these replacement behaviors often focus on communication, self-advocacy, and coping strategies. For instance, a child who bites or hits to avoid completing a task may learn to use their words and ask for a break instead. Techniques such as the behavior moment strategy are often used to build success and confidence while reinforcing a positive change in a child’s behavior.
Ongoing Data Collection and Collaboration
Regularly, ABA teams review data to determine whether their plan is working. Collaboration between families, schools, and trained therapists ensures consistency across environments. Experience has shown that when everyone responds to a behavior in the same way, children learn faster and feel more secure.
How an FBA Leads to a Full Behavior Intervention Plan
The first step in developing a strong BIP is a comprehensive assessment process that identifies why the behavior is occurring.
What the FBA Looks At
A functional behavior assessment evaluates the ABCs in ABA therapy: antecedents (triggers), behaviors, and consequences to uncover functional patterns. It’s this process that supports behavior reduction ABA by encouraging interventions that address root causes rather than merely symptoms. In certain situations, the behaviors in question may be directly linked to a child’s sensory seeking needs, which are carefully considered during the assessment.
Turning Assessment Results into a BIP
Once the assessment data have been collected, they are used to create measurable goals, develop intervention strategies, and design a reinforcement plan. Some BIPs also include detailed breakdowns employing task analysis ABA and crisis or safety plans when appropriate.
Behavior Intervention Plan Example
Example 1: Aggression When Tasks Become Hard
This type of behavior is common in children with autism when task demands exceed their current skill level or coping capacity.
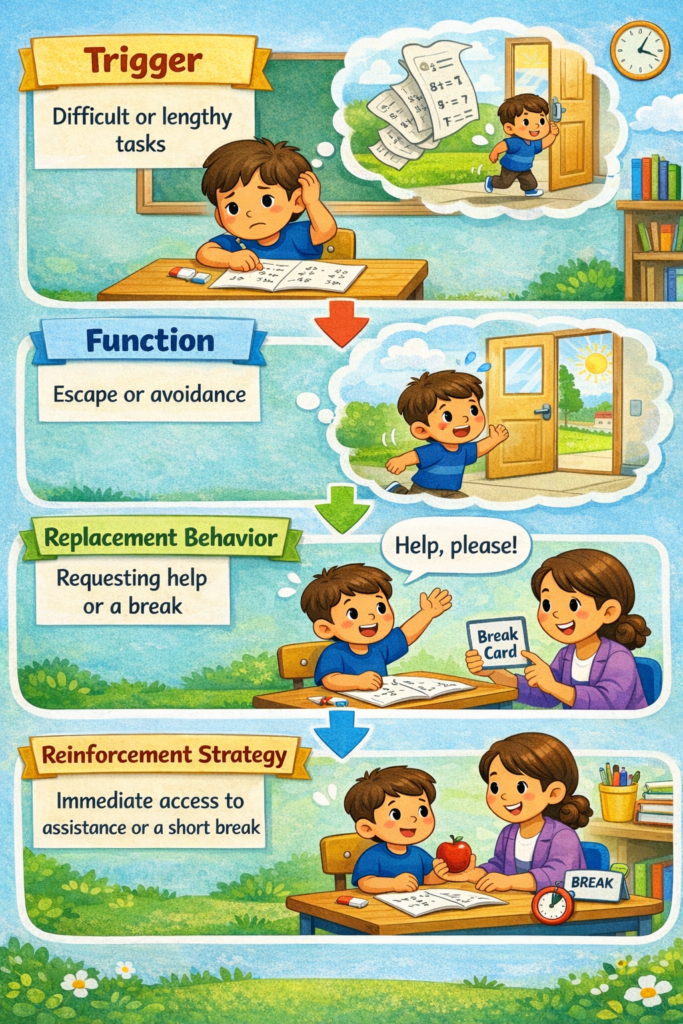
To support success at home, this behavior intervention plan example may also employ structured ABA strategies.
Example 2: Elopement (the act of running away) When Asked to Transition
Transitions can be particularly difficult for autistic children who rely on routine and predictability.

Example 3: Tantrums During Communication Breakdown

How Parents and Teachers Support the BIP at Home and at School
When implemented consistently across environments, a BIP framework is most effective.
Carrying out the Plan at Home
Parents can reinforce the new replacement behaviors, incorporate preventive strategies, and track progress to share with the ABA team at the next meeting.
Using the BIP in the Classroom
When provided with the correct information, teachers can align the BIP with the child’s independent learning plan goals and collaborate with ABA providers. Skills, including social skills therapy, may also be integrated into the child’s school setting.
For more information about ABA providers in your area, contact Heartlinks today.
Common Mistakes Families Can Avoid
One of the most common challenges that families face is inconsistent reinforcement across settings and with different caregivers. When the expectations or responses for a child vary from one situation to another, children may become confused regarding which behaviors will be supported.
Additionally, their progress can be slow when strategies are changed too rapidly before there’s enough data to determine whether the behavior intervention plan is functioning as it was intended.
Finally, not sharing updates with the BCBA, including new triggers for your child, changes at school, or progress at home, can limit the BCBA’s ability to adjust your child’s therapy plan. That’s why ongoing communication and consistency help ensure the BIP remains fluid, responsive, and effective over time.
Reasons Why ABA Teams Review and Update a Behavior Intervention Plan

When the BIP is working with your ABA Provider
Positive progress often appears as reduced frequency or intensity of challenging behaviors, the increased use of replacement skills, and smoother transitions from home to school and community settings. Families and caregivers may also notice improved communication and greater independence throughout daily routines, which indicates that the behavior intervention plan is addressing the behavior’s underlying function.
When Your ABA Team Recommends Plan Adjustments
As children grow and develop, and their environment or demands change, the corresponding goals and strategies must evolve to remain effective. It’s in situations like these that ABA teams may suggest adjustments when progress slows, new skills emerge, or new challenges appear, thereby ensuring the BIP continues to match the child’s needs.
When ABA Clinicians Recommend a New FBA to Complete a New FBA
The need for a new functional behavioral assessment can arise for a number of reasons, including significant changes in behavior patterns, the emergence of new behaviors, or extended plateaus in progress. By reassessing, your child’s therapeutic team can confirm the behavior’s function and if updated interventions are needed.
How ABA Therapists Monitor Progress
To evaluate how well your child’s BIP is working, ABA therapists regularly review their data, gather caregiver and teacher feedback, and continue with ongoing observation. It’s this continuous monitoring that supports timely adjustments and helps maintain consistency across all of your child’s different settings.
To many families, it’s this ongoing review and collaboration that makes a meaningful difference not just on paper, but in everyday life. Parents, like Ashley W., often see progress not only in reduced behaviors but in their child’s confidence, communication, and family routines.
“My daughter has improved tremendously at Heartlinks. Her therapist is such a blessing to us. I love the positivity and dedication of the people who are a part of Heartlinks. Great teamwork!”
Contact Heartlinks ABA to see what changes in your BIP might better support your child.
Get Support Today with a Behavior Intervention Plan ABA
How a BCBA therapist can help
It’s a BCBA therapist who oversees the assessment process, develops and then reviews the behavior intervention plan, and provides ongoing supervision to ensure strategies are correctly implemented. BCBAs also collaborate closely with families, teachers, and other professionals to provide guidance, training, and adjustments to your child’s plan over time.
ABA Therapy Helps Families Build Lasting Skills
With ongoing and consistent implementation and coaching, in-home ABA therapy can help families support skill development in authentic settings where behaviors naturally occur. This approach strengthens communication, daily living skills, and independence by incorporating learning into everyday routines, thereby making progress meaningful and sustainable.
If you’re ready to learn how a BIP ABA works, contact our local ABA therapy in Atlanta, GA, or through any of our other state providers. Call Heartlinks ABA, GA at 410-517-3673 to start home, community, or school support. Our other state providers include:
ABA Charlotte, NC,
Learn how a personalized BIP ABA can support your child at home and at school. Our team is here to help you get started.
